HEALTH National Strategic Plan for Malaria Elimination (2017-2022)
GS PAPER II: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Context: Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare chaired the “Reaching Zero” forum on malaria elimination to celebrate World Malaria Day.
- Every year, 25th April is observed as ‘World Malaria Day’. This year’s theme for the day is “Reaching the Zero Malaria target.’’
National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Malaria Elimination (2017-2022)
- NSP has a vision of a malaria-free country by 2027 and elimination by 2030.
- The National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Malaria Elimination (2017-2022) has been developed based on the National Framework for Malaria Elimination (NFME) of the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP), Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW), Government of India and World Health Organization (WHO) Global Technical Strategy for Malaria Elimination (2016-2030).
Goal
- The goals of NSP strategy are phased elimination of malaria in India.
- National Framework for Malaria Elimination (NFME) in India has set 2030 as eliminating malaria and goals of NSP are in consonance with overall goals
Specific objectives of NSP
- Achieve universal coverage of case detection and treatment services in endemic districts to ensure 100% parasitological diagnosis of all suspected malaria cases and complete treatment of all confirmed cases.
- Strengthen the surveillance system to detect, notify, investigate, classify and respond to all cases and foci in all districts to move towards malaria elimination.
- Achieve near universal coverage of population at risk of malaria with an appropriate vector control intervention.
- Achieve near universal coverage by appropriate BCC activities to improve knowledge, awareness and responsive behavior regarding effective preventive and curative interventions for malaria elimination.
- Provide effective programme management and coordination at all levels to deliver a combination of targeted interventions for malaria elimination.
About Malaria:
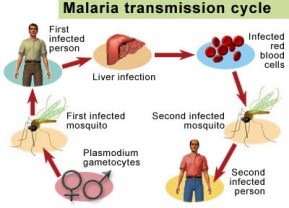
- Malaria is a contagious parasitic disease caused by a parasitic organism called plasmodium and transmitted by mosquito bites.
- There are 5 parasite species that cause malaria in humans, and 2 of these species – P. falciparum and P. vivax – pose the greatest threat.
Causes:
- The disease is caused by the malaria parasite (plasmodium) which is transmitted by an infected female Anopheles mosquito from the infected person to the healthy person.
Other ways of transmitting the disease:
- Pregnant woman may transmit the disease to her fetus. It is also transmitted through blood transfusion.



1.png)
