JAGANNATH TEMPLE ACT

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- In a historic decision, the Odisha state cabinet on Wednesday approved amendments to the Sri Jagannath Temple Act of 1954, simplifying issues pertaining to land owned by the Jagannath Temple.
Jagannath Temple Act, 1954
- After India gained Independence, the state of Odisha formally introduced the Jagannath Temple Act in the year 1952.
- The Act contains provision on land rights of the temple, duties of the sevayat, administrative powers of the Shri Jagannath Temple Managing Committee, rights and privileges of the Raja of Puri and other persons connected with the management and administration of the temple.
Provisions of the recent amendment
- The recent amendment approved by the state cabinet now decentralizes the power to settle land related issues of the temple. The cabinet has delegated power to temple administration and concerned officials for sale and lease of land in name of Jagannath temple.
- Unlike earlier, no approval will be required from the state government for the process.
- Through the sale of land, used and unused, the temple will also generate additional corpus funds.
About the Temple
Location
- The Shree Jagannath Temple is an important Hindu temple dedicated to Jagannath, a form of Vishnu, in Puri in the state of Odisha.
- Puri is one of the four Dhamsor most sacred places of pilgrimages for the Hindus in the country.
Founder
- The temple was built by the Ganga dynasty king Anantavarman Chodaganga in the 12th century CE, as suggested by the Kendupatna copper-plate inscriptionof his descendant Narasimhadeva II.
Festival
- The Puri temple is famous for its annual Ratha yatra, or chariot festival, in which the three principal deities are pulled on huge and elaborately decorated temple cars.
Saints associated
- The temple is sacred to all Hindus and especially in those of the Vaishnava traditions. Many great Vaishnava saints, such as Ramanujacharya, Madhvacharya, Nimbarkacharya, Vallabhacharya and Ramananda were closely associated with the temple.
- Ramanuja established the Emar Mutt near the temple and Adi Shankaracharya established the Govardhana Mutt, which is the seat of one of the four Shankaracharyas.
- It is also of particular significance to the followers of the Gaudiya Vaishnavism whose founder Chaitanya Mahaprabhu, was attracted to the deity, Jagannath, and lived in Puri for many years.
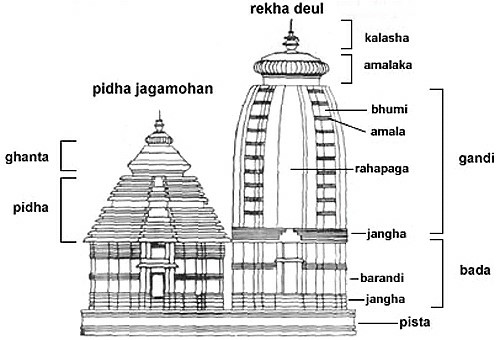
Temple architecture
- The Odisha style of temple architectureis also accorded as Kalinga Nagara style. It is known as White Pagoda.
- The Kalinga Nagara style comprises three typologies i.e. Rekha Deula, Pidha Deula, and Khakhra Deula.
- The famous temple of Lingaraja at Bhubaneshwar and Jagannatha at Puri are two prominent and gigantic examples of Rekha Deula.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/amendment-to-jagannath-temple-act-7708161/



1.png)
