Na-ion batteries
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Scientists have used nano-materials to develop Na-ion-based batteries and supercapacitors which can be rapidly charged and have integrated them in e-cycles.
Sodium-ion battery
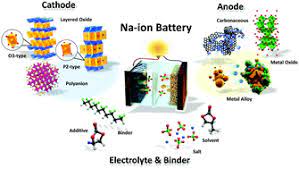
- The sodium-ion battery (NIB or SIB) is a type of rechargeable battery analogous to the lithium-ion battery (LIB) but using sodium ions (Na+) as the charge carriers.
- A typical sodium-ion battery consists of anode, cathode, electrolyte (nonaqueous/aqueous), and a separator. The operation is similar to that of LIBs. In NIBs, the sodium ion is shuttled between positive cathode to negative anode during discharging/charging.
Advantages of Sodium-ion battery over Lithium Ion Batteries
- The low-cost Na-ion-based technologies would be cheap and are expected to reduce the cost of the e-cycles (vehicles)
- High natural abundance of sodium. This would make commercial production of sodium-ion batteries less costly than lithium-ion batteries.
- Sodium-ion batteries have slightly lower energy density, better safety characteristics, and similar power delivery characteristics.
- Sodium-ion batteries do not require many high cost elements required for lithium-ion batteries. Chief among these are lithium, cobalt, copper and nickel.
- So, sodium ion offers a genuine alternative to lithium solutions and will replace lead-acid batteries.

Recent discovery
- Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur has been researching to develop energy storage technologies, which are based on Na-ion, and his team has developed a large number of nanomaterials. The team has used sodium iron phosphates and sodium manganese phosphates which they synthesized to obtain Na-ion-based batteries and supercapacitors. These sodium materials were combined with various novel architectures of carbon to develop a battery.
- These sodium materials are cheaper than Li-based materials, high performing, and can be scaled up to industrial-level production. The Na-ion cell can also be totally discharged to zero volt, similar to a capacitor, making it a safer option in comparison to many other storage technologies. Taking advantage of the fact that Na-ion batteries can be charged rapidly, researchers have integrated it in e-cycles (vehicles) – an easy, affordable option for the general public.
- With further development, the price of these vehicles can be brought down to the range of Rs. 10-15 K, making them nearly 25% cheaper than Li-ion storage technologies-based e-cycles. As disposal strategies of Na-ion-based batteries would be simpler, it can also help in addressing the climate mitigation issue.
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1839574



1.png)
