NATIONAL ACTION PLAN FOR DRUG DEMAND REDUCTION

Copyright infringement not intended
About:
- The Union Government has announced that the government doesn’t have any plan to establish De-addiction Centres at the Village Panchayat level across the country.
- The Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment highlighted that the government implementing a National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) to address the problem of Drug Abuse among the people and youth in the country.
National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR):
- The Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has prepared a National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) for 2018-2023.
- The main strategy is to focus on preventive education, awareness generation, identification, counselling, treatment and rehabilitation of drug-dependent persons and training and capacity building of the service providers through collaborative efforts of the Central and State Governments and Non-Governmental Organizations.
- The Government is taking coordinated action for arresting the problem of substance abuse among the people and youth.
- The government is working with various NGOs for running;
- Integrated Rehabilitation Centres for Addicts (IRCAs)
- Outreach and Drop-in Centres (ODICs)
- Community-based Peer-led Interventions (CPLIs)
- District De-addiction Centres (DDACs)
Main objectives of the NAPDDR:
- Create awareness and educate people about the;
- Ill-effects of drug abuse on the individual, family, workplace and society.
- Reduce stigmatization of and discrimination against, groups and individuals dependent on drugs to integrate them back into society;
- Develop human resources and build capacity to curb drug addiction.
- Facilitate research, training, innovation and collection of relevant information.
- Provide a whole range of community-based services for identification, motivation, counselling, and de-addiction.
- Formulate and implement comprehensive guidelines, schemes, and programmes using a multiagency approach for drug demand reduction;
- Initiate drug demand reduction efforts to address all forms of drug abuse.
Drug abuse in India
- Drug addiction is spreading fast among Indian youth. According to a survey by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, India has more than 70 million drug addicts.
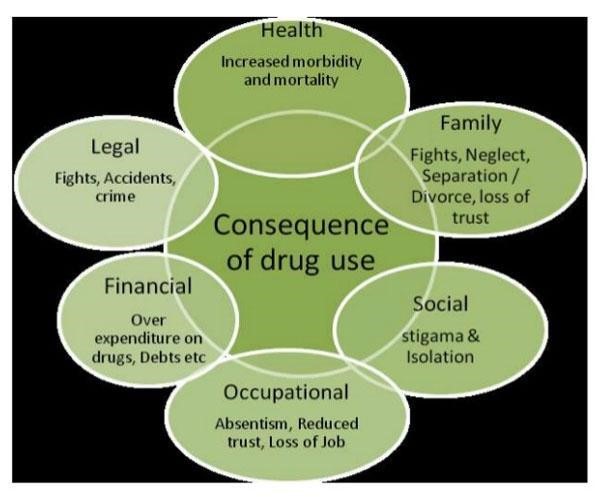
- It is a serious health problem which not only destroys the person involved but his entire family, society and the nation.
- It promotes anti-social behaviour such as stealing, crime and violence.
- It affects the economic growth of a country by generating unaccounted money that is also used for terror funding and anti-national activities.
- Therefore it is also a serious threat to national security.
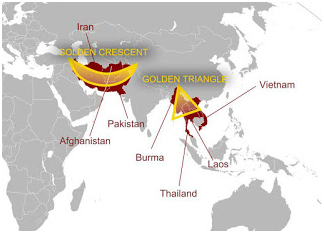
- India is located between the two largest Opium producing regions of the world;
- Golden triangle on the eastern side: Thailand, Myanmar, Vietnam and Laos.
- Golden crescent on the North-Western side: Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran.
As per the report released by the All India Institute Of Medical Science (AIIMS):
- More than 5 crore Indians have reported using cannabis and opioids.
- Nearly 8.5 lakh people inject drugs.
- More than half of the total registered cases are from Punjab, Assam, Delhi, Haryana, Manipur, Mizoram, Sikkim and Uttar Pradesh.
Steps taken by the Government:
- The Indian government is Coordinating with Various International Organizations including BRICS, SAARC, ASIAN, etc, to share information and intelligence to combat transnational drug trafficking.
- Coordinating among Various Central and State Agencies:
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs has launched the SIMS (Seizure Information Management System) Portal for the digitization of pan-India drug seizure data.
- The National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse was constituted to meet the expenditure incurred in connection with combating illicit traffic in Narcotic Drugs; rehabilitating addicts, educating the public against drug abuse, etc.
- Project Sunrise was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to tackle the rising HIV prevalence in northeastern states in India, especially among people injecting drugs.
- ‘Nasha Mukt Bharat’ or Drug-Free India Campaign with a focus on community outreach programs.
- India is a signatory of the following International treaties and conventions;
- United Nations (UN) Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961).
- UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971).
- UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (1988).
- UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) 2000.
Way Forward:
- Article 47 of the Directive Principles of State Policy of the Constitution of India directs the state to improve public health and endeavour to bring about the prohibition of the consumption of intoxicating drinks and drugs which are injurious to health.
- Steps need to be taken to stop cross-border trafficking and improve the enforcement of law in India.
- The stigma associated with drug taking needs to be reduced.
- Society needs to understand that drug addicts are victims and not criminals.
- Proper Counseling is another alternative.
- The education curriculum should include topics on drug addiction, its impact and also on de-addiction.
- Enhancing skills of care providers.
- Funding for evidence-based interventions.
- Developing programmes for vulnerable groups like youth, street children, women, prisons, etc




.jpeg)


1.png)
