





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Findings and projections
GDP
Formula for Calculating GDP
There are three different ways that economists and statisticians can calculate a country’s GDP and they should all, theoretically, produce the same number:
This is calculated using the formula:
GDP = consumption (C) + investment (I) + government spending (G) + (exports (X) - imports (M)).
4 Types of GDP
There are four different types of GDP and it is important to know the difference between them, as they each show different economic outlooks.
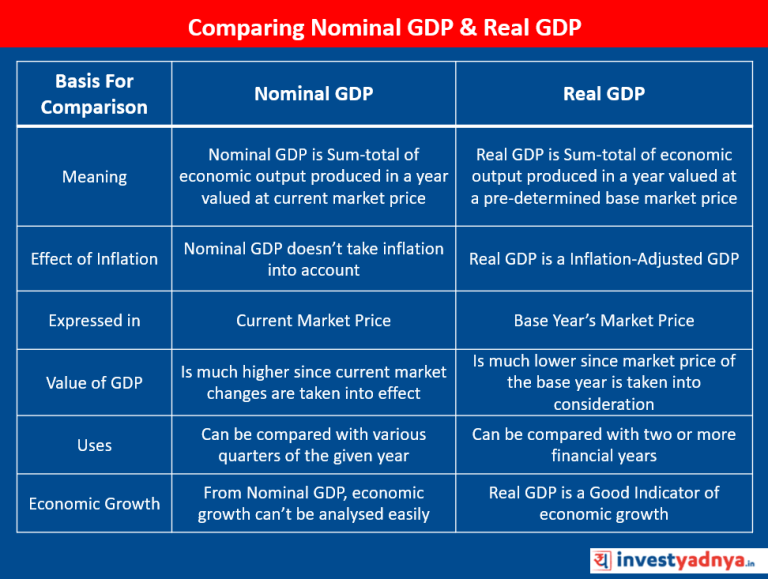
Nominal GDP is calculated with inflation (i.e without removing the effect of rising prices). The prices of goods and services are calculated at current price levels. It is defined as a GDP measure, expressed in absolute terms. The raw GDP data, before inflation adjusted is called Nominal GDP. It includes all the changes in the prices of finished goods and services that took place in one year due to inflation or deflation.
Real GDP is a calculation of GDP that is adjusted for inflation (removing the effect of rising prices). The prices of goods and services are calculated at a constant price level, which is usually set by a predetermined base year. Real GDP is considered the most accurate portrayal of a country’s economy and economic growth rate. It exclusively considers the production and free from price changes or currency fluctuations.
GDP deflator is a factor by which Nominal GDP is adjusted to calculate Real GDP. It adjusts gross domestic product by removing the effect of rising prices. It shows how much an economy’s GDP is really growing.
Formula is : GDP Deflator = ( Nominal GDP / Real GDP ) * 100
Actual GDP is the measurement of a country’s economy at the current moment in time.
Potential GDP is a calculation of a country’s economy under ideal conditions, like a steady currency, low inflation, and full employment.
Gross National Product (GNP)
Net National Product (NNP)
Unlike GDP, GNP, net national product (NNP) may also be categorized as:
NNPmp = NNPfc – S + (IT+ GS) or,
NNPmp = NNPfc – subsidies + (indirect tax+ surpluses from government enterprises)
NNPfc = NNPmp + S - (IT+ GS) or,
NNPfc = NNPmp + subsidies - (indirect tax+ surpluses from government enterprises)
Normally, NNP at market prices is higher than NNP at factor cost because indirect taxes exceed government subsidies. However, NNP at market prices can be less than NNP at factor cost when government subsidies exceed indirect taxes.
Some other concepts of national income
Private income
Private income is income obtained by private individuals from any source, produce or otherwise and retained income of corporations. It can be obtained from NNP at factor cost by making certain additions and deductions.
Private Income = National income (NNP at factor cost) +Transfer Payments + Interest on Public Debt – Social Security – Profits and Surpluses of Public Undertakings.
Personal Income
Personal income is the total income received by the individuals of a country from all sources before direct taxes in one year. Personal income is never equal to the national income because the former includes the transfer payments whereas they are not included in national income. Personal income is derived from national income by deducting undistributed corporate profits, profit taxes, and employee’s contributions to social security schemes. Personal income is differs than private income actually it is less than private income because it excludes undistributed corporate profits.
Personal Income = National Income – Undistributed Corporate Profits – Profit Taxes – Social Security Contributions + Transfer Payments + Interest on Public Debt.
Disposable Income
Disposable income or personal disposable income means the actual income which can be spent on consumption by individuals and families.
Disposable Income = National Income – Business Savings – Indirect taxes plus Subsidies – Direct Taxes on persons – Direct Taxes on Business – Social Security Payments + Transfer Payments + Net Income from Abroad (X-M).
Real Income
Real Income is the income expressed in terms of a general level of prices of a particular year taken as base year. National income in terms of money at current prices does not indicate the real state of the economy. So the concept of real income has been propounded to rectify such illusions. This is also known as National Income at constant prices.
Real NNP = NNP for the Current Year Multiply with Base Year Index (100) Divided by Current Year Index.
Per Capita Income
The average income of the people of a country in a particular year is called Per Capita Income for that year.
Per Capita Income for 2011 = National Income for 2011 divided by Population in 2011
This concept enables us to know the average income and the standard of living of the people.
But it is not very reliable due to unequal distribution of national income exist in every country.
|
NATIONAL STATISTICAL COMMISSION The National Statistical Commission (NSC) of India is an autonomous body which formed in June 2005 under the recommendation of Rangarajan commission. The Chairperson of the Commission enjoys the status of a Minister of State and the Members of the Commission have the status equivalent to the Secretary to the Government of India. Mandate: To collect, coordinate, collate and disseminate credible and timely statistics for informed decision making and debate, within and outside the Government. The objective of its constitution is to reduce the problems faced by statistical agencies in the country in relation to collection of data. |
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/key-economic-concepts-back-to-basics








© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved