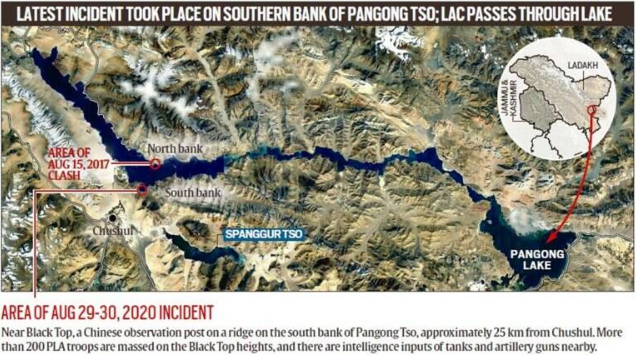
Pangong Tso.
Context: India and China have unsettled borders, and the perception of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) differs in multiple sectors, including on Pangong Tso.
About Pangong Tso:
- Pangong Tso is an endorheic lake (landlocked) that is partly in India’s Ladakh region and partly in Tibet. The name reflects the mixed heritage of the lake: Pangong in Ladakhi means extensive concavity, the word Tso is Tibetan for lake. Situated at an elevation of about 4,270 m, it is a nearly 135-km long, narrow lake — 6 km at its widest point — and shaped liked a boomerang. Its total area is over 600 sq km.
- The Karakoram Mountain range, which crosses Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, China and India, with heights of over 6,000 metres including K2, the world’s second highest peak, ends at the north bank of Pangong Tso. Its southern bank too has high broken mountains sloping towards Spangur Lake in the south.
- The lake’s water, while crystal clear, is brackish, making it undrinkable. The lake freezes during the winter, allowing some vehicular movement on it as well.
Reference: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-importance-of-pangongs-south-bank-6578044/



1.png)
