REPORT ON BEST PRACTICES IN THE PERFORMANCE OF DISTRICT HOSPITALS

Disclaimer: No copyright infringement of images intended.
Context
- NITI Aayog released a performance assessment report of district hospitals in India, titled Best Practices in the Performance of District Hospitals.
About
- The report is an outcome of collaboration with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and WHO India.
- The National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers, a constituent board of the Quality Council of India, conducted the on-ground data validation.
- This report is the first-ever performance assessment of district hospitals undertaken across the country.
- The Health Management Information System (HMIS) data for the year 2017–18 has been used as baseline for this exercise.
- The framework classifies hospitals in three categories: Small Hospitals (less than or equal to 200 beds), Mid-sized Hospitals (between 201–300 beds) and Large Hospitals (more than 300 beds).
Findings
- Overall, 75 district hospitals across 24 States and Union Territories emerged as top performers on indicators ranging from availability of beds, medical and paramedical staff, core health and diagnostic testing services to outputs such as bed occupancy rate and number of surgeries per surgeon.
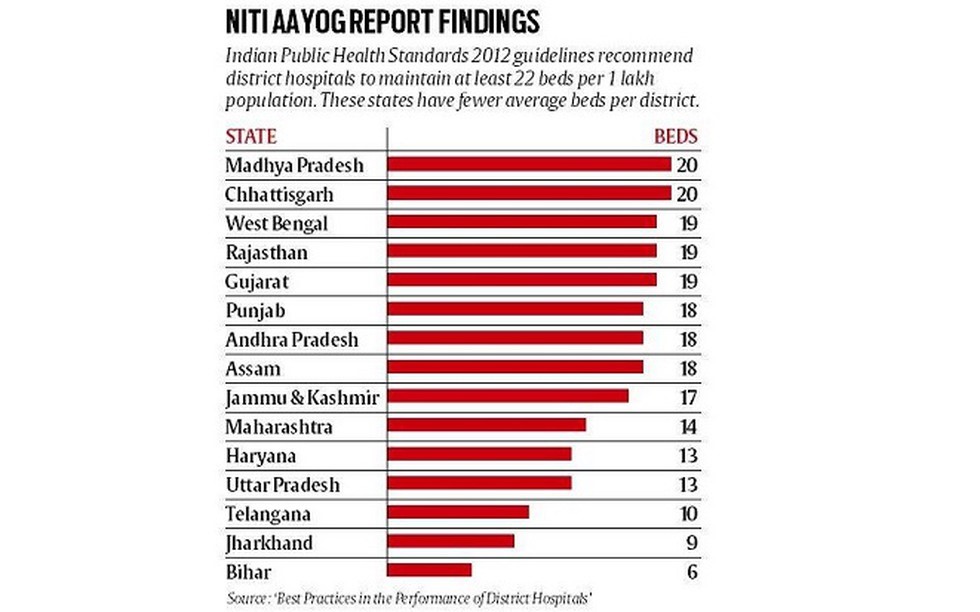
- On an average a district hospital in India has 24 beds per 1 lakh population.
- The Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) 2012 guidelines recommend district hospitals to maintain at least 22 beds per 1 lakh population (based on district population average of 2001 Census)
- Thus, the average number of beds per lakh population in a district hospital was higher than the recommended figure of 22 beds per lakh of population across 21 states and Uts
- District hospitals in India have a range of 1 to 408 beds per 1 lakh population.
- The report highlights some key issues faced by the health system and provides some sustainable solutions to strengthen the condition of district hospitals in the country, primarily involving improving data reporting in HMIS, and encouraging such performance assessment exercises to bring about greater accountability for health care services in district hospitals.
Significance
- This report can serve as a foundation for a roadmap of action for developing upgraded and improved district hospitals in the country.



1.png)
