RTI Pleas
Copyright infringement not intended
In News
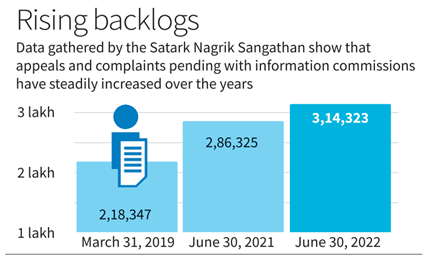
- According to a report by Satark Nagrik Sangathan, nearly 3.15 lakh complaints and appeals are pending before 26 information commissions across India.
- The highest number of pending cases (99,722) was in Maharashtra, followed by Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka.
Details
- The report says information commissions in Jharkhand and Tripura have been not functioning for 29 months and 15 months respectively.
- Only 5% of all positions in commissions are occupied by women.
- Several information commissions, including the Central Information Commission, are working with a shortage of manpower.
- Out of the total of 165 posts of information commissioners, 42 are vacant, including two chief State information commissioners.
Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005
- The Right to Information Act requires timely responses to citizen requests for Public authority.
- There is no defined format of application for pursuing information.
- The information seeker is not required to provide reasons for asking for information.
- The main objective is to empower the citizens, promote transparency and accountability in the working of the Government, curb corruption, etc.
- Under the act, Information is any material in any form.
- It includes records, documents, memos, e-mails, press releases, circulars, orders, logbooks, contracts, reports, papers, samples, models, and data.
- A “Public authority” means any authority or body or institution of self-government established or constituted;
- by or under the Indian Constitution.
- by any other law made by the Indian Parliament.
- by any other law made by State Legislature.
- by notification issued or order made by the Government, and includes any body owned, controlled or substantially financed.
- Public Authorities publish the rules, regulations, instructions, manuals and records.
- He publishes facilities available to citizens for obtaining information.
- He provides reasons for its administrative or quasi-judicial decisions to affected persons.
- Types of information exempted from RTI
- Which would affect the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security, strategic, scientific or economic interests of the State, and affect the relation with foreign States.
- Which may constitute contempt of court.
- Anything under the Official Secrets Act, of 1923.
- Intelligence and security organisations are specified in the 2nd Schedule.
Central Information Commission
- It is the statutory body constituted under the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005.
- They are the final appellate authority for RTI Act.
- Central Information Commission consists of a Chief Information Commissioner and not more than 10 Information Commissioners (IC).
- They are appointed by the President on the recommendation of a committee consisting of;
- The Prime Minister.
- The Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha.
- A Union Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM.
- They shall not be Members of Parliament or Members of the Legislature of any State or Union Territory as the case may be, or hold any other office of profit or connected with any political party or carry on any business or pursue any profession.
- They are not eligible for reappointment.
- The tenure, salary and allowances of the information commissioners are not fixed.
- RTI Amendment Act, 2019 has empowered the Central Government to notify them.
- They are required to submit annual reports to the Parliament through the Ministry of Personnel and Training.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=G3VACOMPU.1&imageview=0
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9




1.png)
