RUSSIA’S INVASION OF UKRAINE
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov made a statement about the status of the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Current status of invasion
- President Vladimir Putin with his ‘special military operation’ indicated to counter militarization and Nazification in Ukraine.
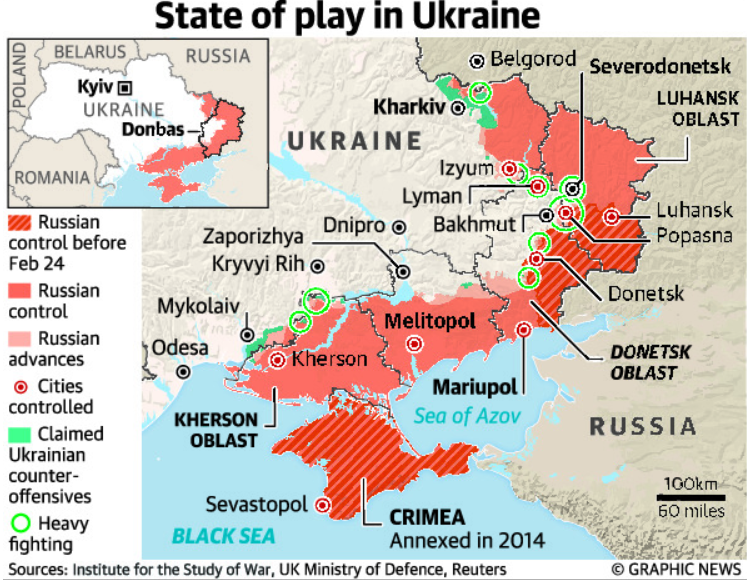
- Russia started the war on February 24 on three fronts — its troops moved in from the Belarussian border in the north, from the separatists-controlled parts of Donbas in the east and the Russian-controlled Crimean Peninsula in the south.
- Russia controls from the south, the city of Kherson and the nuclear plant near Zaporizhzhia. In the eastern Donbas region, they have taken almost all major cities including Mariupol. They are currently advancing towards Severodonetsk.
What does Russia want?
- With the goal of demilitarization and de-Nazification, Russia is aiming to establish its economic and cultural relations in the region. Therefore, Russia has planned to control areas where it has core interests:
- The liberation of Donbas was Russia’s unconditional priority as it is the traditional industrial region that has historical ties with Russia.
- Luhansk and Donbas oblasts (province) were declared sovereign states before the invasion.
- Whereas, Donetsk including Mariupol will help Russia to establish a land bridge from the Russian mainland to Crimea along the Sea of Azov.
- And by controlling Mariupol, Russia will achieve its second, de-Nazification as the region is also the headquarters of the Azov Battalion, the neo-Nazi group that had been integrated into the Ukrainian armed forces.
- Russian Commander, Maj Den Rustam Minnekayev, indicated that Russia aspires to control the whole of Ukraine’s east and south which would turn Ukraine into a landlocked country.
Sanction on Russia
- The Russian economy was expected to contract this year; however, the sanctions had a limited impact on the Russian economy for multiple reasons:
- The western response to the ongoing war has bolstered Mr Putin’s standing in Russia as 82% of Russians approve of his presidency.
- The sanctions led to an increase in all the commodity prices and as a major exporter of oil and gas, the Russian currency is proved to be one of the best-performing currencies this year.
- With Russian blockade of Ukraine’s seaports is threatening a surge in prices and hence could hamper the global supply and food security. Countries outside of Western alliances (including European countries) are reaching out to Russia for a solution. Hence, the west was never able to isolate Russia.
Way forward
- Multiple rounds of talks were concluded between both the countries. In the last round of the Istanbul talks, Ukraine had made a peace proposal.
- In the peace proposal, Ukraine proposed a 15-year consultation period for Crimea (Ukraine will not claim the region) and a direct talk between both the leaders on the status of Donbas.
- Even Russia announced to withdraw of troops from the outskirts of Kyiv. But, with the USA accusing Russia of committing genocide in Ukraine, the peace process collapsed.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GBB9SAVH0.1&imageview=0



1.png)
