SSLV D2

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully instituted the second edition of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV-D2) from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
Launch vehicle
- A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket-propelled vehicle used to carry a payload from Earth's surface to space, usually to Earth orbit or beyond.
SSLV
- About:The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (or SSLV) is a small-lift launch vehicle being developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Aim:The SSLV was developed with the aim of launching small satellites commercially at drastically reduced price and higher launch rate as compared to Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- Capacity and Features:It has a payload capacity to deliver 600 kg. SSLV is a three-stage, all-solid launch vehicle that can carry a payload weighing 500 kilograms to the polar orbit, 500 kilometers above Earth's surface and a 300-kilogram payload into Sun Synchronous Polar Orbit. It has the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs. The SSLV is the smallest vehicle at 110-ton mass at ISRO. It can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit while the tried and tested PSLV can launch satellites weighing in the range of 1000 kg.

Must Read: https://iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/small-satellite-launch-vehicle-47
SSLV-D2
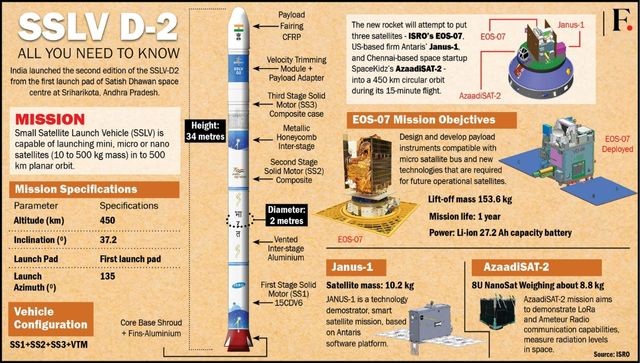
- Configured with three solid propulsion stages and a velocity terminal module, the rocket “caters to the launch of up to 500 kg satellites to low Earth orbits on a launch-on-demand basis.
- It provides low-cost access to space, offers low turn-around time and flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites, and demands minimal launch infrastructure.
- Built and realised by ISRO, the primary satellite earth observation satellite (EOS-07) weighs 156.3 kg.
- EOS-07 – which has a mission life of one year – was designed so that its “payload instruments are compatible with microsatellite buses and new technologies that are required for future operational satellites.
- Technology demonstrator satellite, Janus-1, is developed by United States-based Antaris and its Indian partners XDLinks and Ananth Technologies.
- Weighing 10.2 kg, Janus-1 is a six-unit satellite carrying five payloads.
- The payloads of AzaadiSAT-2 have been built by 750 girl students from across India.
- According to ISRO, the satellite aims to demonstrate LoRa and amateur radio communication capabilities, assess radiation levels in space, and exhibit an expandable satellite structure.
Final Thoughts
- The objective of launching SSLV was to showcase the “in-flight performance” of its vehicle systems.
- The SSLV was built to meet the needs of the emerging small and microsatellite commercial market and offer launches on demand.




.jpeg)

1.png)
