TITAN
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Saturn’s moon Titan holds liquid lakes, rivers and fields of sand dunes, much like Earth. But the ingredients that make up the landscapes of the two worlds are different.- Study.
Details
- Titan’s sand dunes — rounded piles of sand deposited by the wind — contain hydrocarbons, unlike sand on Earth.
- The hydrocarbon grains that make up Titan’s landscape are soft and brittle. They remain grain-sized.
- Titan is one of the 82 moons orbiting Saturn. Methane lakes and sand dunes dot Titan.
- The research team turned to sediments on Earth called ooids — rounded, sand-sized particles of calcium carbonate found in shallow tropical seas — to find answers.
- The moon is dry around the equator while its poles are wet due to an abundance of methane lakes.
- At the equator, sand transport occurs primarily by winds, indicating the presence of fine sand grains — an ingredient of sand dunes.
|
Ooids in Titan Ooids form when calcium carbonate from the water attaches in layers around a grain, such as quartz, the report noted. While ooids grow as the mineral solidifies from a solution, they also break down when grains are smashed into each other by waves and storms. This process ensures the size stays constant, the researchers highlighted. Something similar can be playing out on Titan, too, the researchers speculated. The hydrocarbon sediments might break down during their transport through wind or methane rivers. They are likely to grow back as fragments combine to form sand-sized grains during rest. |
- NASA believes Titan can be potentially habitable. The moon’s atmosphere contains roughly 95 per cent nitrogen and 5 per cent methane. The air is so dense that humans will not need a pressure suit to walk on the surface, according to the space agency.
- Its atmosphere is also conducive to the type of prebiotic chemistry [organic compounds] that may have given rise to life on Earth.
- Humans, however, cannot survive on Titan without an oxygen mask and the moon’s average temperature is minus 179 degrees Celsius, according to NASA.
About Titan
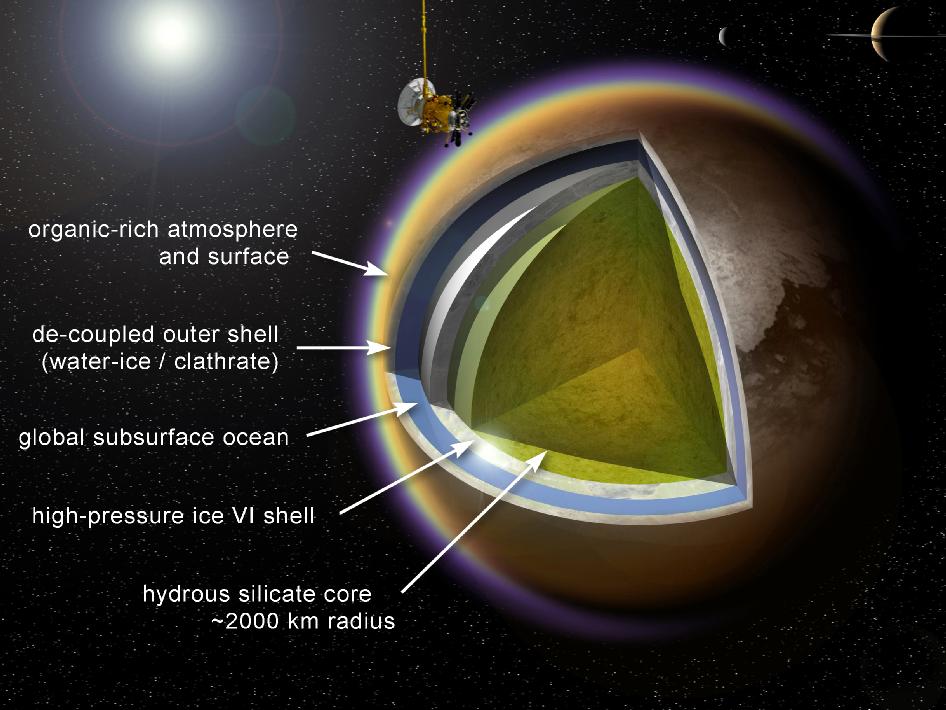
- Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second-largest natural satellite in the Solar System.
- It is the only moon known to have a dense atmosphere, and is the only known object in space other than Earth on which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found.
- Titan is 50% larger (in diameter) than Earth's Moon and 80% more massive. It is the second-largest moon in the Solar System after Jupiter's moon Ganymede, and is larger than the planet Mercury, but only 40% as massive.
- Titan is 50% larger (in diameter) than Earth's Moon and 80% more massive. It is the second-largest moon in the Solar System after Jupiter's moon Ganymede, and is larger than the planet Mercury, but only 40% as massive.
- The atmosphere of Titan is largely nitrogen; minor components lead to the formation of methane and ethane clouds and heavy organonitrogen haze.
- The climate—including wind and rain—creates surface features similar to those of Earth, such as dunes, rivers, lakes, seas (of liquid methane and ethane).
- With its liquids (both surface and subsurface) and robust nitrogen atmosphere, Titan's methane cycle bears a striking similarity to Earth's water cycle, albeit at the much lower temperature of about 94 K (−179 °C; −290 °F).



1.png)
